item 13. clone 재정의는 주의해서 진행하라.
clone() 메소드는 무엇일까?
글이 긴 것은 가독성이 좋지 않기 때문에 clone을 정리해서 블로그에 정리해놨다.
clone() 메소드를 배우기에 앞서 얕은 복사와 깊은 복사의 개념을 숙지하면 좋을 것 같아서 정리해봤다.
Cloneable 인터페이스의 역할
- cloneable은 클래스을 복제를 할 수 있는지 확인하기위한 용도로 쓰인다. → 이런 인터페이스를
minxin interface라고 부른다.
💡 mixin (믹스인)이란?
- 클래스가 본인의 기능 이외에 추가로 구현할 수 있는 자료형으로, 어떤 선택적 기능을 제공한다는 사실을 선언하기 위해 쓰인다.
clone의 규약
1. x.clone() ≠ x
→ 반드시 true
2. x.clone().getClass() == x.getClass()
→ 반드시 true
3. x.clone().equals(x)
→ true일 수도 있고 아닐 수도 있다.
4. x.clone.getClass() == x.getClass()
관례상, 반환된 객체와 원본 객체는 독립적이어야 한다. 이를 만족하려면 super.clone으로 얻은 객체의 필드 중 하나 이상을 반환 전에 수정해야 할 수도 있다.
가변상태를 참조하지 않는 clone 정의
- 가변 상태를 참조하지 않는 클래스용 clone 메서드
@Override
public PhoneNumber clone() {
try {
return (PhoneNumber) super.clone();
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
throw new AssertionError(); // 일어날 수 없는 일.
}
}
- 원래 clone의 모습
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneSupportedException {
return super.clone();
}
어떤 클래스(Object)를 상속받아서 Overriding을 할 때, 접근 지시자는 상위 클래스에 있는 접근지시자와 같거나 더 넓은 범위의 접근 지시자를 가져야한다.
💡 공변 반환 타이핑(convariant return typing)
- 메서드를 Overriding(재정의)할 때 재정의 된 메서드의 반환 타입이 상위 클래스의 메서드가 반환하는 하위 유형이 될 수 있다 라는 것
- 공변 반환 타이핑 예제

공변 반환 타이핑의 장점
- clone()이라는 메소드를 호출하는 부분에서
타입 캐스팅을 하지 않아도된다.
가변 객체를 참조하는 clone 메소드 재정의
- 아래의 예제(서적에 나온 예제)로 설명을 하겠습니다.
import java.util.Arrays;
// Stack의 복제 가능 버전 (80-81쪽)
public class Stack implements Cloneable {
private Object[] elements;
private int size = 0;
private static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 16;
public Stack() {
this.elements = new Object[DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY];
}
public void push(Object e) {
ensureCapacity();
elements[size++] = e;
}
public Object pop() {
if (size == 0)
throw new EmptyStackException();
Object result = elements[--size];
elements[size] = null; // 다 쓴 참조 해제
return result;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size ==0;
}
// 원소를 위한 공간을 적어도 하나 이상 확보한다.
private void ensureCapacity() {
if (elements.length == size)
elements = Arrays.copyOf(elements, 2 * size + 1);
}
@Override public Stack clone() {
try {
Stack result = (Stack) super.clone();
return result;
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
throw new AssertionError();
}
}
}
가변 객체의 clone 구현하는 방법
Cloneable인터페이스를 구현해야한다.clone()메소드를 재정의해야한다. → 재정의할 때,protected→public으로 변경해주고, return 타입을Object에서 클래스 타입으로 변경해준다.super.clone()호출해준다.
3번까지는 가변 상태를 참조하지 않는 clone 하고 같다.
이제 아래부터는 가변 객체의 clone 구현 방법을 알아보자.
가변 객체에서 clone을 구현할 떄 주의해야할 것들.
stack, copy -> elementsS[0, 1]→ stack과 copy(result) 동일한 elements를 참조한다. 즉, 다른 인스턴스에서 동일한 배열을 참조하는 것이 된다.
따라서 원본이나 복제본 중 하나를 수정하게 된다면 다른 하나도 수정되어 불변식의 깨뜨린다. → 불안한 코드다.

public static void main(String[] args) {
Object[] values = new Object[2];
values[0] = new PhoneNumber(123, 456, 7890);
values[1] = new PhoneNumber(321, 764, 2341);
Stack stack = new Stack();
for (Object arg : values)
stack.push(arg);
Stack copy = stack.clone();
System.out.println("-----pop from stack-----");
while (!stack.isEmpty())
System.out.println(stack.pop() + " ");
System.out.println("-----pop from copy-----");
while (!copy.isEmpty())
System.out.println(copy.pop() + " ");
System.out.println("-----같은 인스턴스 인가요?-----");
System.out.println(stack.elements[0] == copy.elements[0]); // 같은 인스턴스 확인 하는 코드
}
결과 :
-----pop from stack-----
321-764-2341
123-456-7890
-----pop from copy-----
null
null
-----같은 인스턴스 인가요?-----
true
위와 같이 결과가 stack에서 pop을 했는데 copy에도 영향을 준다.
- 위의 코드를 극복하려면
result.elements = elements.clone()를 추가 해준다. →얕은 복사
코드를 추가해주면, 인스턴스는 동일하지만 각각 배열을 만들어서 복사를 한다. 하지만 얕은 복사이기때문에 인스턴스는 같다. 실제 배열 안에 인스턴스까지 완전히 새로운 복사를 하는 것이 아니다.
따라서 인스턴스를 조작한다면, copy()를 갖고 있는 PhoneNumber클래스에 영향을 준다. → 불안한 코드
@Override
public Stack clone() {
try {
Stack result = (Stack) super.clone();
result.elements = elements.clone(); // 추가된 소스 코드
return result;
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
throw new AssertionError();
}
}
result.elements = elements.clone()추가할 경우 결과
-----pop from stack-----
321-764-2341
123-456-7890
-----pop from copy-----
321-764-2341
123-456-7890
-----같은 인스턴스 인가요?-----
true
같은 인스턴스이지만 각각 배열을 만드는 방식으로 바뀐다.
불안전한 방법이다. 다른 방법을 알아보자.
가변 상태를 갖는 클래스용 재귀적 clone메서드 재정의
- 위의 코드보다 나은 방법 →
깊은 복사(deep copy)
package me.chapter03.item13;
public class HashTable implements Cloneable {
private Entry[] buckets = new Entry[10];
private static class Entry{
final Object key;
Object value;
Entry next;
public Entry(Object key, Object value, Entry next) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.next = next;
}
public void add(Object key, Object value) {
this.next = new Entry(key, value, null);
}
// 재귀적 방법
public Entry deepCopy(){
return new Entry(key, value, next == null ? null : next.deepCopy());
}
// ---------shallow copy---------
// @Override
// protected HashTable clone() {
// HashTable result = null;
// try{
// result = (HashTable) super.clone();
// result.buckets = this.buckets.clone(); // p82. shallow copy이기 때문에 위험하다.
// return result;
// }catch(CloneNotSupportedException e){
// throw new AssertionError();
// }
// }
// ---------deep copy---------
@Override
public HashTable clone() {
HashTable result = null;
try {
result = (HashTable) super.clone(); // 배열을 clone이 아닌 직접만듬.
result.buckets = new Entry[this.buckets.length]; // clone용 buckets 배열
for (int i = 0; i < this.buckets.length; i++) {
if (buckets[i] != null) {
result.buckets[i] = this.buckets[i].deepCopy(); // p83. deep copy
}
}
return result;
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
throw new AssertionError();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashTable hashTable = new HashTable();
Entry entry = new Entry(new Object(), new Object(), null);
hashTable.buckets[0] = entry;
HashTable clone = hashTable.clone();
System.out.println(hashTable.buckets[0] == entry); // true
System.out.println(hashTable.buckets[0] == clone.buckets[0]); //true
}
}
public Entry deepCopy(){
return new Entry(key, value, next == null ? null : next.deepCopy());
}
Entry의 deepCopy 메서드는 재귀적 방법을 사용하고 있다.
이때 Entry의 deepCopy 메서드는 자신이 가리키는 연결 리스트 전체를 복사하기 위해 재귀방법을 쓴다.
하지만
이 방법에는 문제점이 있다.
재귀 호출 때문에 리스트의 원소 수만큼 스택 프레임을 소비하여, 리스트가 길면 스택 오버플로를 일으킬 위험이 있기 때문이다.
이 방법을 피하기 위해 사용하는 것이 반복자 를 사용하는 것이다.
- Entry 자신이 가리키는 연결 리스트를 반복적으로 복사한 코드
public Entry deepCopy(){
Entry result = new Entry(key, value, next);
for(Entry p = result ; p.next != null ; p = p.next){
p.next = new Entry(p.next.key, p.next.value, p.next.next);
}
return result;
}
- 반복자를 사용한 결과
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashTable hashTable = new HashTable();
Entry entry = new Entry(new Object(), new Object(), null);
hashTable.buckets[0] = entry;
HashTable clone = hashTable.clone();
System.out.println(hashTable.buckets[0] == entry); // true
System.out.println(hashTable.buckets[0] == clone.buckets[0]); // false
}
Clone 메서드 주의 사항
- 일반적으로 상속용 클래스에 Clonealbe 인터페이스 사용을 권장하지 않는다. 해당 클래스를 확장하려는 프로그래머에게 많은 부담을 주기 때문이다.
상속을 쓰기 위한 클래스 설계 방식 두 가지가 있다. 알아보자…
1️⃣Cloneable을 직접 구현해주고 하위클래스가 구현을 안해도 되게하는 방법
/**
* p84, p126 일반적으로 상속용 클래스에 Clonealbe 인터페이스 사용을 권장하지 않는다.
* 해당 클래스를 확장하려는 프로그래머에게 많은 부담을 주기 때문이다.
*
*/
public abstract class Shape implements Cloneable {
private int area;
public abstract int getArea();
/**
* p84. 부담을 덜기 위해서는 기본 clone() 구현체를 제공하여, Cloneable 구현 여부를 서브(하위) 클래스가 선택할 수 있다.
* @return
* @throws CloneNotSupportedException
*/
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
return super.clone();
}
}
2️⃣하위 클래스에서 Cloneable을 구현을 못하게 하는 방법 → final
@Override
protected final Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
return super.clone();
}
3️⃣clone()을 구현할 때 고수준의 API를 사용해서 재정의한다.
- put, get 등을 말한다.
- 객체는 super.clone()이 만들고, 그 객체의 모든 필드는 고수준API를 통해서 데이터 접근을 한다. → 단점 저수준 보다는 처리속도가 느리다.
result = (HashTable)super.clone(); //객체를 만듬
result.get(key)
result.put(key, value)
이 마지막을 이야기하기 위해서 앞에 빌드업을 했다..
실질적으로 쓰이는 방법
- 복사 생성자
- 복사 팩터리
이 두 가지를 사용한다. 앞서 이야기한 것들을 극복해주는 방법들이다..
1️⃣복사 생성자
public class HashSetExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set<String> hashSet = new HashSet<>();
hashSet.add("Dante");
hashSet.add("DeokRin");
System.out.println("HashSet: " + hashSet);
Set<String> treeSet = new TreeSet<>(hashSet);
System.out.println("TreeSet: " + treeSet);
}
}
TreeSet 생성자로 hashset을 받는다. 엄격히 말하자면 Collection으로 받는다. 그리고 생성자에서 copy를 해준다.
- TreeSet 생성자
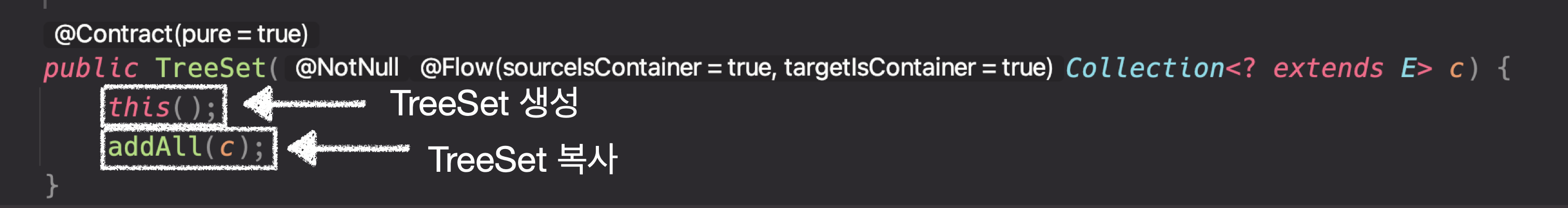
복사 생성자의 장점
- 생성자를 쓰면 좋은점은
명확해진다는 것이다.- clone() 메소드는 생성자를 써서 만들지 않기 때문에 어떻게 만들어지는지 불명확하기 때문에 좋지않다.
final을 사용할 수 있다.- clone() 메소드 때문에 final을 못쓰는 것은 손실이 크다. 따라서 생성자를 쓰면 앞서 설정을 해주기 때문이다.
- 해당 클래스가 구현한 ‘인터페이스’ 타입의 인스턴스를 인수로 받을 수 있다.
- 모든 범용 컬렉션 구현체는 Collection이나 Map 타입을 받는 생성자를 제공한다.